Introduction
Building a full-stack application is not just about functionality and performance — security is equally critical. From frontend (React, Angular, Vue) to backend (Django, Node.js, Laravel) and database layers, vulnerabilities can appear anywhere if proper precautions aren’t taken.
In this blog, we’ll explore common security vulnerabilities in full-stack apps and discuss best practices to prevent them.
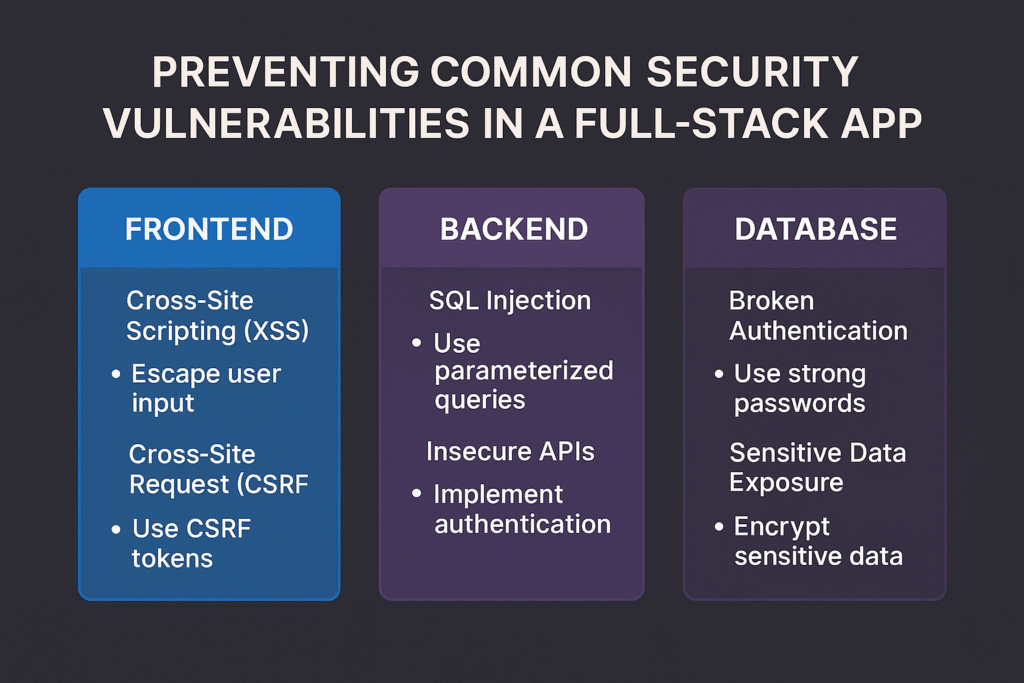
1. SQL Injection (SQLi)
What it is:
Attackers insert malicious SQL queries into input fields to manipulate databases.
Example (Vulnerable Code):
# ❌ Vulnerable
query = f"SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = '{email}' AND password = '{password}'"
cursor.execute(query)
How to Prevent:
- Use parameterized queries or ORM methods.
- Example with Django ORM:
# ✅ Safe
user = User.objects.filter(email=email, password=password).first()
- Validate and sanitize inputs.
2. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
What it is:
Attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages, which execute in other users’ browsers.
Example:
<input type="text" value="<script>alert('Hacked!')</script>">
How to Prevent:
- Always escape user input in frontend and backend.
- Use libraries like DOMPurify in React to sanitize HTML.
- Set Content Security Policy (CSP) headers to restrict scripts.
3. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
What it is:
Tricks authenticated users into performing unwanted actions (like transferring funds).
How to Prevent:
- Use CSRF tokens in forms (Django and Rails include this by default).
- Example in Django:
<form method="POST">
{% csrf_token %}
<input type="text" name="amount">
<button type="submit">Transfer</button>
</form>
- Use SameSite cookies (
Set-Cookie: sessionid=...; SameSite=Strict).
4. Broken Authentication & Session Management
What it is:
Weak authentication flows allow attackers to hijack accounts.
How to Prevent:
- Use JWT or OAuth2 with proper expiration.
- Store tokens in HTTP-only, secure cookies (not localStorage).
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Enforce strong password policies & rate limiting.
5. Insecure APIs
What it is:
APIs that expose too much data or lack authentication can be exploited.
How to Prevent:
- Use rate limiting & API throttling (e.g., Django REST Framework throttling, Express rate limiter).
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC).
- Return only necessary fields (avoid over-fetching sensitive data).
- Secure endpoints with HTTPS + authentication headers.
6. Insecure File Uploads
What it is:
Attackers upload malicious files (scripts, malware) disguised as images/documents.
How to Prevent:
- Validate file type and size on both frontend and backend.
- Store files in cloud storage (e.g., S3) instead of executing from server.
- Rename files with UUIDs and never allow direct execution.
7. Sensitive Data Exposure
What it is:
Sensitive information (API keys, passwords) is leaked in frontend code or error logs.
How to Prevent:
- Store secrets in environment variables (e.g.,
.env). - Hash passwords with strong algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2.
- Use HTTPS/TLS everywhere.
- Mask sensitive fields in logs.
8. Security Misconfigurations
What it is:
Default settings, open ports, or missing security headers leave apps vulnerable.
How to Prevent:
- Disable debug mode in production (
DEBUG=Falsein Django,NODE_ENV=productionin Node.js). - Add security headers:
X-Frame-Options: DENYContent-Security-PolicyStrict-Transport-Security
- Keep dependencies updated and use vulnerability scanners (e.g., Snyk, Dependabot).
9. Denial of Service (DoS/DDoS)
What it is:
Attackers overload the system with traffic or expensive operations.
How to Prevent:
- Implement request rate limiting.
- Optimize queries and avoid long-running operations on the main thread.
- Use CDNs and load balancers for traffic distribution.
10. Best Practices for Full-Stack Security
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) — users and services should only have the minimum access they need.
- Automate security testing with CI/CD pipelines.
- Use Web Application Firewalls (WAF) for additional protection.
- Regularly conduct penetration testing and code audits.
- Educate developers about OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Securing a full-stack app requires attention at every layer — from frontend input validation and backend API security to database protection and infrastructure hardening.
By addressing common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, XSS, CSRF, and authentication flaws, developers can ensure their applications are resilient against real-world attacks.