Introduction
When building modern applications on AWS, an API Gateway often serves as the front door for clients interacting with backend services. Whether you’re running serverless applications with AWS Lambda, containerized apps with ECS/EKS, or microservices on EC2, the Amazon API Gateway plays a critical role in managing API traffic, security, and performance.
However, as applications scale, unoptimized API Gateways can become a bottleneck—increasing latency, inflating costs, and affecting user experience. This blog explores strategies to optimize API Gateway performance for high-traffic, enterprise-grade AWS deployments.
Why Optimize API Gateway?
- Reduce Latency – Faster response times improve user experience.
- Cost Efficiency – Minimize unnecessary API calls and over-provisioning.
- Scalability – Handle thousands of concurrent requests seamlessly.
- Security & Control – Protect APIs with throttling and authentication.
- Reliability – Prevent outages by balancing loads effectively.
Key Optimization Strategies
1. Enable API Caching
- API Gateway provides built-in caching at the stage level.
- Cache frequent responses to reduce backend load.
- Example: Instead of hitting the database for every request, return cached results for repeated queries.
✅ Benefits: Reduced latency, fewer Lambda/database invocations.
⚡ Tip: Adjust cache TTL to balance freshness vs. performance.
2. Use Request Throttling and Rate Limiting
- Protect backend services from overload by setting:
- Burst Limits (max requests per second).
- Rate Limits (steady-state throughput).
- Prevents sudden spikes from affecting availability.
✅ Benefits: Better resiliency and cost control.
3. Leverage AWS Lambda with Provisioned Concurrency
- Cold starts in Lambda functions can add latency.
- Use Provisioned Concurrency to keep instances warm.
- Combine with API Gateway for real-time, low-latency responses.
✅ Best for: High-traffic APIs that need consistent performance.
4. Optimize Payload Size
- Reduce request/response payloads with compression (gzip/brotli).
- Avoid sending large unused fields.
- For file uploads/downloads, use pre-signed S3 URLs instead of routing through API Gateway.
✅ Benefits: Faster responses, lower data transfer costs.
5. Use Regional Endpoints or Edge-Optimized Endpoints
- Edge-Optimized (default): Routes traffic via CloudFront CDN, ideal for global apps.
- Regional Endpoints: Best for APIs serving users in a specific AWS region.
- Choose based on user geography.
✅ Benefits: Lower latency and reduced unnecessary hops.
6. Integrate with AWS WAF and Cognito
- Secure APIs by enabling AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall) for protection against attacks.
- Use Amazon Cognito for authentication & authorization.
✅ Benefits: High security without custom implementation.
7. Implement Logging & Monitoring with CloudWatch
- Enable detailed metrics for latency, 4xx/5xx errors, and cache hit ratios.
- Set CloudWatch Alarms to detect anomalies in API traffic.
- Use X-Ray tracing to identify bottlenecks in backend services.
✅ Benefits: Proactive troubleshooting and performance tuning.
8. Deploy Multiple Stages & Versions
- Use stages (dev, staging, prod) with unique endpoints.
- Support versioning to avoid breaking changes.
- Deploy canary releases for safe rollouts.
✅ Benefits: Safer deployments and backward compatibility.
9. Combine with API Gateway v2 (HTTP APIs)
- For lower-cost and faster APIs, use HTTP APIs (v2) instead of REST APIs (v1).
- HTTP APIs offer:
- Up to 70% lower latency
- Up to 70% cheaper cost
- Ideal for simple use cases with JWT auth and Lambda integrations.
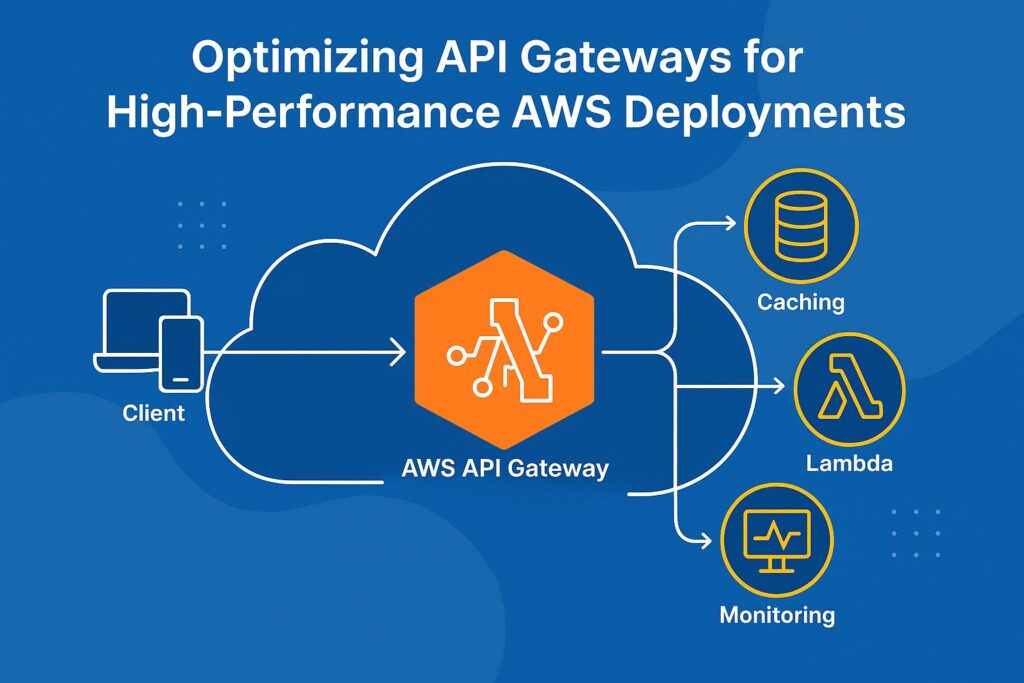
Example Architecture
- Client → API Gateway
- API Gateway → AWS Lambda / ECS Services
- Database (DynamoDB, RDS, MongoDB Atlas on AWS)
- Caching with CloudFront + API Gateway
- Monitoring via CloudWatch + X-Ray
This ensures speed, reliability, and scalability.
Best Practices
- Use fine-grained IAM policies for API security.
- Enable stage variables for environment-specific configs.
- Prefer asynchronous processing (SQS, SNS, EventBridge) for heavy workloads.
- Regularly review API Gateway limits and request quotas.
- Combine with CloudFront caching for global distribution.
Conclusion
Optimizing API Gateway is essential for high-performance AWS deployments. By leveraging caching, throttling, payload optimization, and monitoring, you can significantly reduce latency, protect backend resources, and enhance user experience.
Whether running serverless apps, microservices, or hybrid architectures, a well-optimized API Gateway ensures your system remains fast, secure, and cost-efficient as traffic grows.








3 Responses
Let’s spread the love! Tag a friend who would appreciate this post as much as you did.
Your positivity and optimism are contagious It’s impossible to read your blog without feeling uplifted and inspired Keep up the amazing work
Let’s spread the love! Tag a friend who would appreciate this post as much as you did.