Introduction
In today’s digital world, users expect applications to load instantly. Slow response times not only harm user experience but also affect engagement, conversions, and revenue. One of the most effective ways to boost performance is through caching.
Caching stores frequently accessed data in a faster storage layer (like memory) so that future requests can be served more quickly. In a full-stack application, caching can be applied at multiple layers: client-side, server-side, and database.
This blog explains types of caching, best practices, and tools you can use to make your full-stack applications scalable and efficient.
1. What is Caching?
Caching is the process of storing data temporarily so it can be quickly retrieved without recomputing or re-fetching from the main source.
For example:
- Instead of querying a database for the same product details repeatedly, you can cache it in Redis or browser storage for faster access.
2. Benefits of Caching
- Improved performance → Faster response times.
- Reduced server load → Fewer repeated computations or queries.
- Cost efficiency → Lower database and API calls.
- Scalability → Handles high traffic more efficiently.
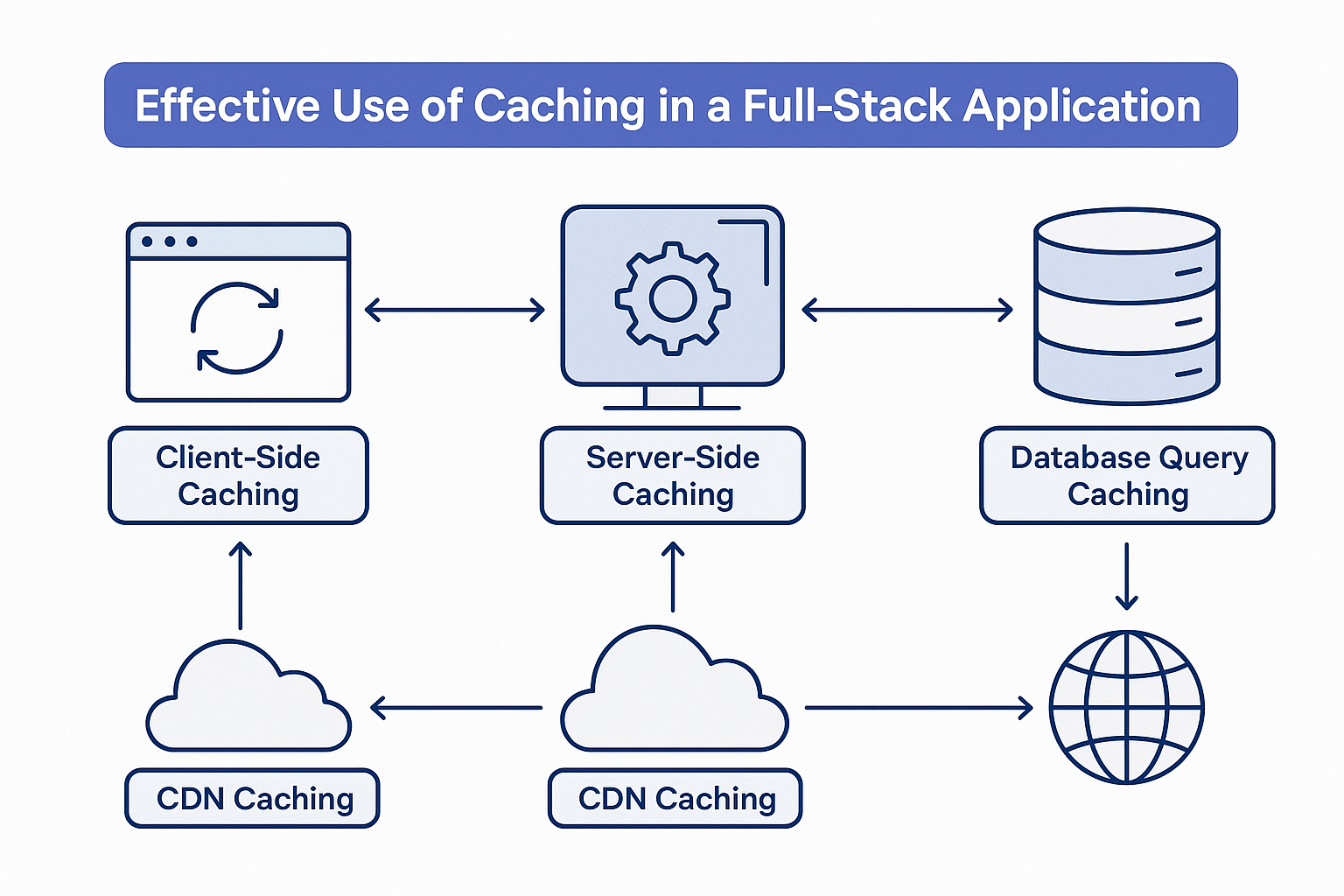
3. Types of Caching in Full-Stack Applications
a) Client-Side Caching
- Browser cache: Stores static assets (HTML, CSS, JS, images).
- Service Workers: Enable offline support with Progressive Web Apps (PWA).
- LocalStorage/SessionStorage: Store user preferences, tokens, or frequently accessed data.
Example (saving API response in LocalStorage):
function getUserData() {
const cached = localStorage.getItem("userData");
if (cached) return JSON.parse(cached);
return fetch("/api/user")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
localStorage.setItem("userData", JSON.stringify(data));
return data;
});
}
b) Server-Side Caching
- In-memory caching using Redis or Memcached.
- Reverse proxy caching using Nginx or Varnish.
- Application-level caching with frameworks like Django, Node.js, or Laravel.
Example (Django + Redis caching):
from django.core.cache import cache
def get_event(event_id):
key = f"event_{event_id}"
event = cache.get(key)
if not event:
event = Event.objects.get(id=event_id)
cache.set(key, event, timeout=300)
return event
c) Database Query Caching
- Store frequent query results in cache to reduce database load.
- Use materialized views or query caching plugins (e.g., MySQL query cache, PostgreSQL pgpool-II).
Example (SQL with Redis):
def get_top_products():
products = redis.get("top_products")
if products:
return json.loads(products)
products = db.query("SELECT * FROM products ORDER BY sales DESC LIMIT 10")
redis.set("top_products", json.dumps(products), ex=600)
return products
d) CDN Caching (Content Delivery Network)
- CDNs like Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront, or Akamai cache static assets globally.
- Reduces latency by serving content from the nearest server.
- Ideal for images, videos, CSS, and JS files.
4. Best Practices for Caching
- Cache only what’s necessary – Avoid caching volatile or sensitive data.
- Set expiration (TTL) – Ensure stale data gets refreshed periodically.
- Use cache invalidation – Update or remove outdated cache entries when data changes.
- Layered caching – Combine client-side, server-side, and database caching.
- Monitor cache hit ratio – Ensure caching is improving performance, not just adding complexity.
5. Tools and Technologies for Caching
- Client-side: LocalStorage, IndexedDB, Service Workers.
- Server-side: Redis, Memcached, Nginx, Varnish.
- Database: PostgreSQL pgpool-II, MySQL query cache.
- CDN: Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront, Fastly.
6. Example: Full-Stack Caching Flow
- React frontend → Caches user data in LocalStorage.
- Node.js/Django backend → Uses Redis to cache API responses.
- Database → Query results cached in Redis.
- CDN → Static assets cached globally.
This multi-layer caching strategy reduces load and improves responsiveness for users worldwide.
Conclusion
Effective caching is critical for building high-performance, scalable full-stack applications. By strategically applying client-side, server-side, database, and CDN caching, you can significantly reduce load times and enhance user experience.