Introduction
Event management systems need to handle a wide range of operations — from user registrations and ticket sales to scheduling, notifications, and analytics. The API layer plays a crucial role in connecting the frontend with the backend efficiently.
Traditionally, developers have relied on REST APIs, but GraphQL has emerged as a modern alternative offering more flexibility. In this blog, we’ll compare GraphQL vs REST in the context of event management systems, their advantages, challenges, and when to use each.
1. What is REST API?
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an architectural style for building APIs. It uses HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to perform operations on resources.
Example (REST Endpoint for Events):
GET /api/events→ Get all eventsGET /api/events/123→ Get event detailsPOST /api/events→ Create a new event
Pros of REST:
- Simple and widely adopted.
- Caching supported via HTTP.
- Works well for CRUD-based applications.
Cons of REST:
- Over-fetching or under-fetching data (retrieving more or less than needed).
- Multiple endpoints needed for complex data queries.
2. What is GraphQL?
GraphQL is a query language for APIs developed by Facebook. Unlike REST, it allows clients to ask for exactly the data they need.
Example (GraphQL Query for Event and Attendees):
{
event(id: "123") {
name
date
location
attendees {
name
email
}
}
}
Pros of GraphQL:
- Fetch exactly what you need (no over-fetching).
- Single endpoint for all queries.
- Strongly typed schema.
- Great for mobile and frontend-heavy apps.
Cons of GraphQL:
- Higher learning curve.
- Caching is more complex.
- Can lead to performance issues if queries aren’t optimized.
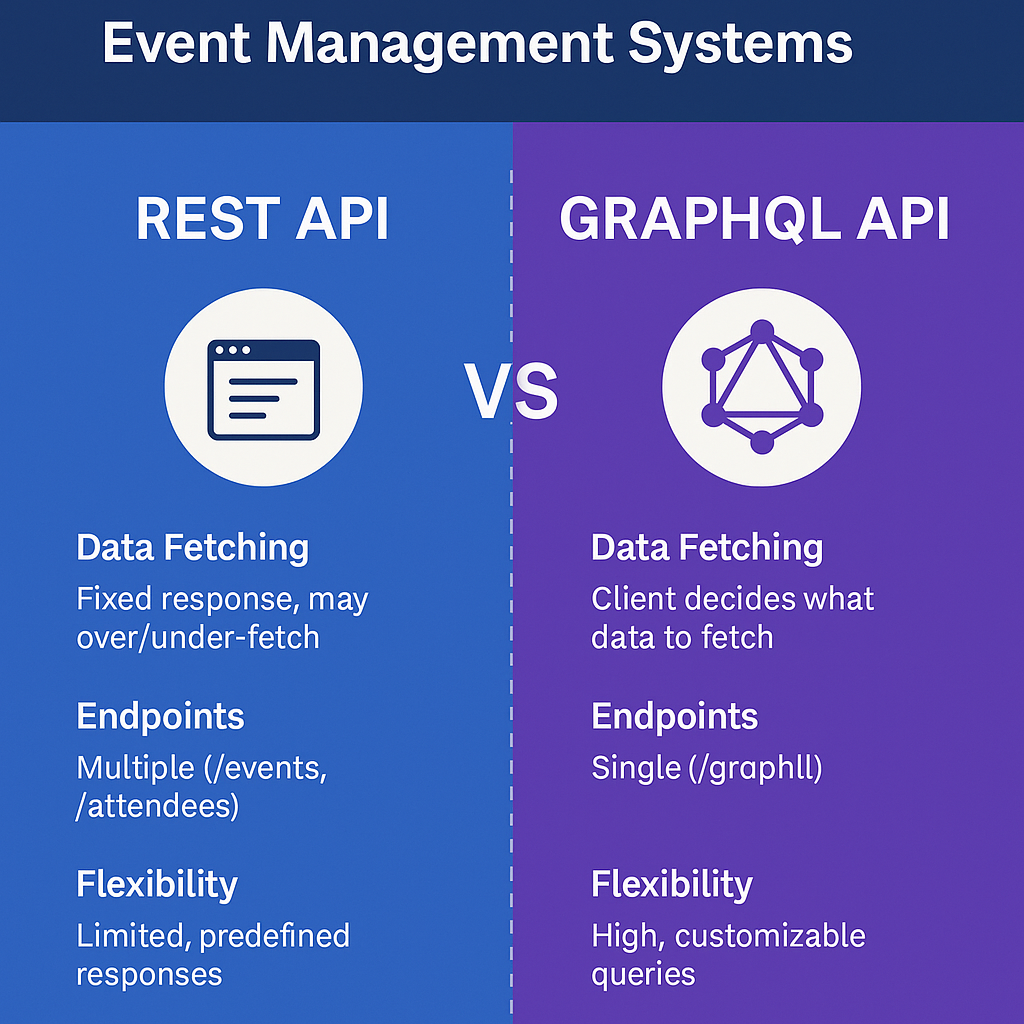
3. Comparing GraphQL vs REST in Event Management Systems
| Feature | REST API | GraphQL API |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fetching | Fixed response, may over/under-fetch | Client decides what data to fetch |
| Endpoints | Multiple (/events, /attendees) | Single (/graphql) |
| Flexibility | Limited, predefined responses | High, customizable queries |
| Performance | Good with caching, may require multiple requests | Optimized for fewer round-trips |
| Ease of Use | Simple, familiar to most developers | Requires schema design, learning curve |
| Tooling | Mature ecosystem, works with HTTP tools | Strong developer tools (GraphiQL, Apollo) |
| Caching | Built-in with HTTP | Requires custom strategies |
4. Example Use Cases
✅ When to Use REST for Event Management
- Small to medium-sized event systems.
- Simple CRUD operations (create events, update schedules).
- Applications where caching performance is critical.
- Teams already experienced with REST APIs.
Example: A local workshop platform with basic ticket booking and schedules.
✅ When to Use GraphQL for Event Management
- Large-scale systems with complex relationships (events, attendees, sponsors, speakers).
- Mobile or React/Angular-based apps needing customized data fetching.
- Applications with rapidly evolving requirements.
- Multi-device support (desktop, mobile, smartwatch).
Example: A global conference platform showing personalized schedules, speaker details, and live updates.
5. Hybrid Approach
Many modern applications combine both:
- Use REST for simple CRUD and public APIs.
- Use GraphQL for complex data fetching and client customization.
For example, an event management system may:
- Use REST for payment gateways (
/payments). - Use GraphQL for attendee dashboards (fetching user-specific sessions, tickets, and notifications in one query).
Conclusion
Both GraphQL and REST have their place in building event management systems.
- Choose REST if you need simplicity, caching, and mature ecosystem support.
- Choose GraphQL if you need flexible data fetching, fewer requests, and better frontend integration.
- For most real-world event platforms, a hybrid approach delivers the best balance of performance and flexibility.