Introduction
Event management systems handle large volumes of data — from registrations and payments to notifications and live updates. Traditionally, these operations required servers that needed constant monitoring and scaling. However, with AWS Lambda, organizations can adopt a serverless architecture that is cost-effective, scalable, and easier to maintain.
In this article, we’ll explore how AWS Lambda fits into event management systems, its benefits, and real-world use cases.
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. You simply upload your function, and AWS handles the execution, scaling, and fault tolerance automatically.
Key highlights:
- Pay per execution – you’re charged only when your code runs.
- Automatic scaling – handles thousands of requests per second.
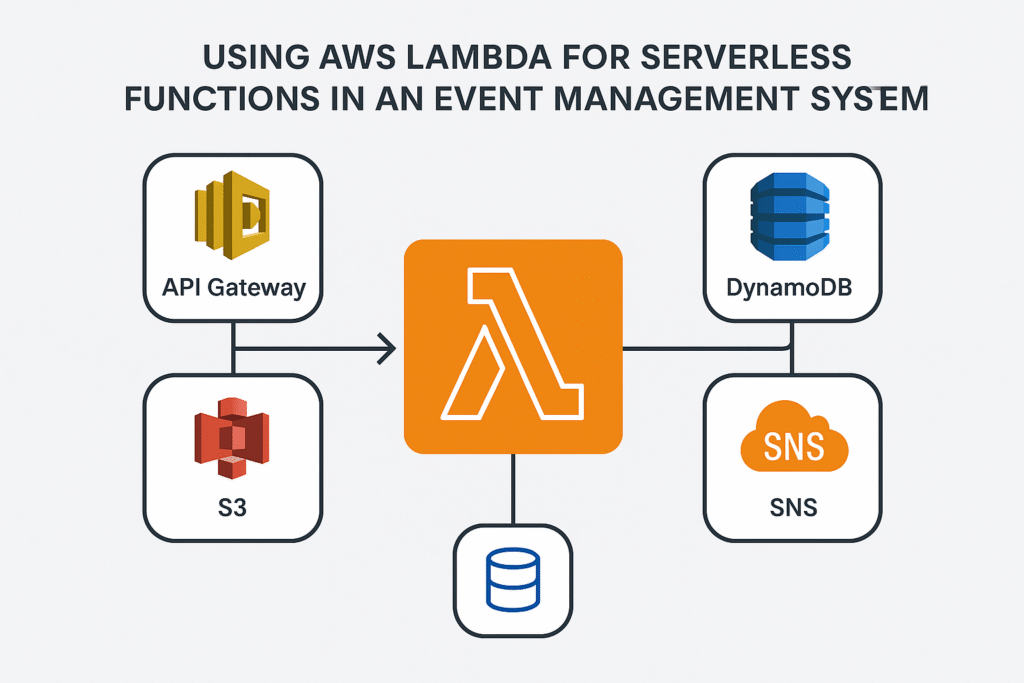
- Event-driven – integrates seamlessly with AWS services like S3, DynamoDB, SNS, and API Gateway.
Why Use AWS Lambda for Event Management Systems?
- Scalability:
Event management often deals with unpredictable traffic spikes (e.g., concert ticket sales or conference registrations). Lambda scales automatically based on demand. - Cost Efficiency:
Instead of running idle servers, you only pay for the execution time, making it ideal for seasonal events. - Flexibility:
Integrates with multiple AWS services like S3 for file uploads, DynamoDB for registrations, SNS for notifications, and API Gateway for REST APIs. - Faster Development:
Teams can deploy small, independent functions quickly without worrying about infrastructure management.
Use Cases of AWS Lambda in Event Management Systems
1. User Registration Handling
- Trigger: API Gateway receives a registration request.
- Lambda Function: Validates input, stores user details in DynamoDB, and sends a confirmation email via Amazon SES.
2. Payment Processing
- Trigger: A payment request from the frontend.
- Lambda Function: Calls the payment gateway API (Stripe/PayPal), verifies transaction success, and updates user registration.
3. Real-Time Notifications
- Trigger: Event schedule changes or announcements stored in DynamoDB.
- Lambda Function: Publishes messages via SNS or Firebase to send SMS, emails, or push notifications to attendees.
4. Ticket Generation & QR Codes
- Trigger: Successful registration/payment.
- Lambda Function: Generates a unique QR code ticket and stores it in S3, with a link emailed to the attendee.
5. Post-Event Analytics
- Trigger: Data upload to S3 after the event.
- Lambda Function: Processes data (registrations, attendance, feedback) and stores insights in Amazon Redshift for reporting.
Step-by-Step: Implementing AWS Lambda in Event Management
Step 1: Create a Lambda Function
- Go to AWS Console → Lambda → Create Function.
- Choose Author from scratch.
- Select a runtime (Node.js, Python, Java, etc.).
- Write your function code (e.g., handling registrations).
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
dynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')
table = dynamodb.Table('EventRegistrations')
# Extract user data from request
user_data = json.loads(event['body'])
table.put_item(Item=user_data)
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps({'message': 'Registration successful!'})
}
Step 2: Expose Function with API Gateway
- Create a REST API in Amazon API Gateway.
- Connect API routes (e.g.,
/register) to the Lambda function. - Enable CORS for frontend integration.
Step 3: Connect to Other AWS Services
- DynamoDB → Store user data.
- S3 → Store tickets, invoices, or event files.
- SNS/SES → Send confirmations & updates.
- CloudWatch → Monitor logs and execution metrics.
Benefits Recap
- No server management → AWS handles scaling and uptime.
- Highly available → Functions run across multiple availability zones.
- Cost-efficient → Pay only for execution time.
- Modular & flexible → Different microservices can be handled independently.
Conclusion
By leveraging AWS Lambda in an event management system, organizations can streamline operations such as registrations, ticketing, payments, and notifications without worrying about infrastructure. This serverless approach not only ensures scalability and resilience but also reduces costs dramatically.








One Response
I like this web site because so much utile stuff on here : D.